Bridging the gap Combining Cloud and On-Premise Security with C4SAM...
Read MoreCritical vulnerability in the Shim boot loader
What to do?
A critical vulnerability in the Shim boot loader, affecting most Linux distributions, has been identified and addressed by the release of version 15.8. Discovered by Bill Demirkapi, the flaw (CVE-2023-40547) could allow remote code execution and bypass Secure Boot. Major distributions like Debian, Red Hat, SUSE, and Ubuntu have issued advisories. The vulnerability stems from HTTP protocol handling, potentially leading to system compromise. Exploiting it grants early-stage access during the boot process, enabling attackers to deploy bootkits for extensive control. Additionally, version 15.8 fixes five other vulnerabilities with various implications, emphasizing the need for prompt updates to secure systems.
What to do?
First, you need to understand if you are affected.
This can’t be done by an blackbox-scan from an central instance as Vulnerability scanners do it today without local agent or remote access with high privileged permissions. It’s easy and much faster to access the system software in C4SAM’s inventory function and query for shim software versions:
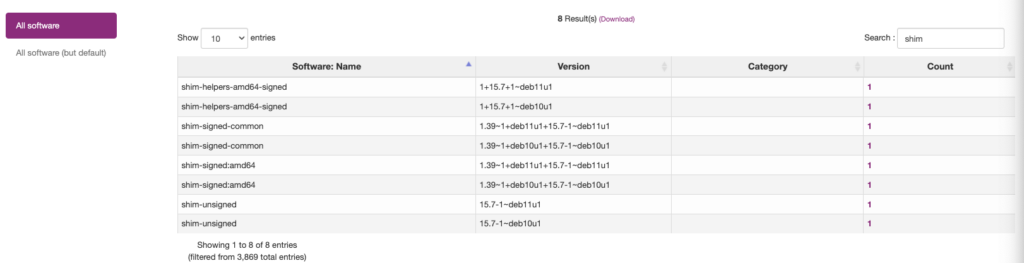
All Linux systems are vulnerable below Shim version 15.8. To mitigate this issue, it is recommended to patch the systems with the released patches and execute the OS command “fwupdmgr”. Alternatively, reconfiguring the bootloader, specifically grub2, to avoid using Shim can also help.
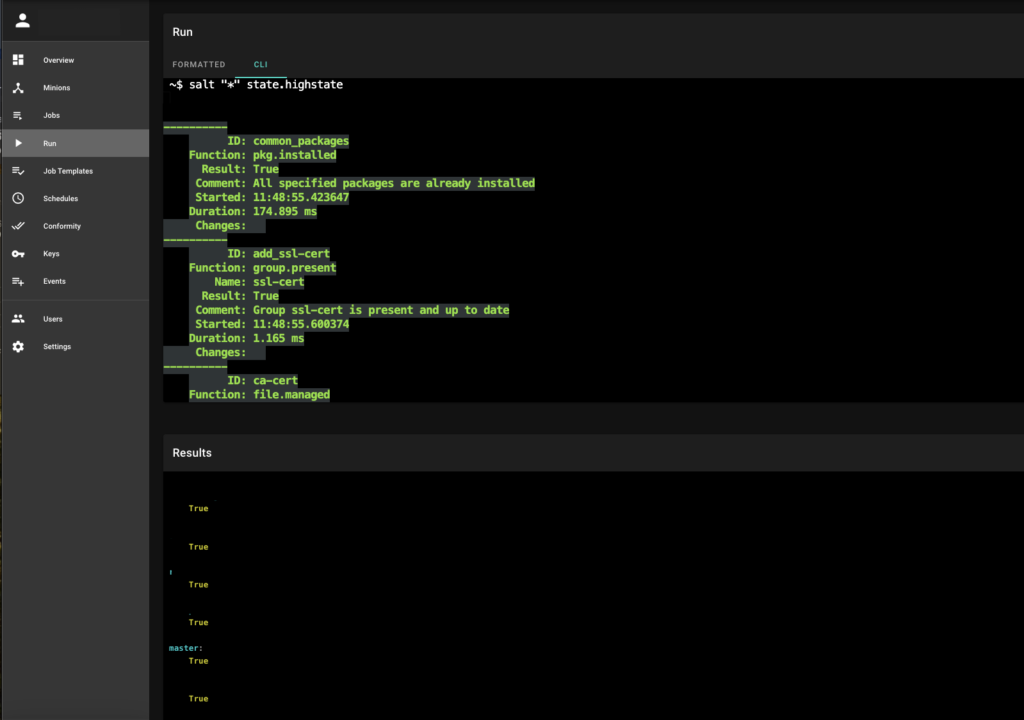
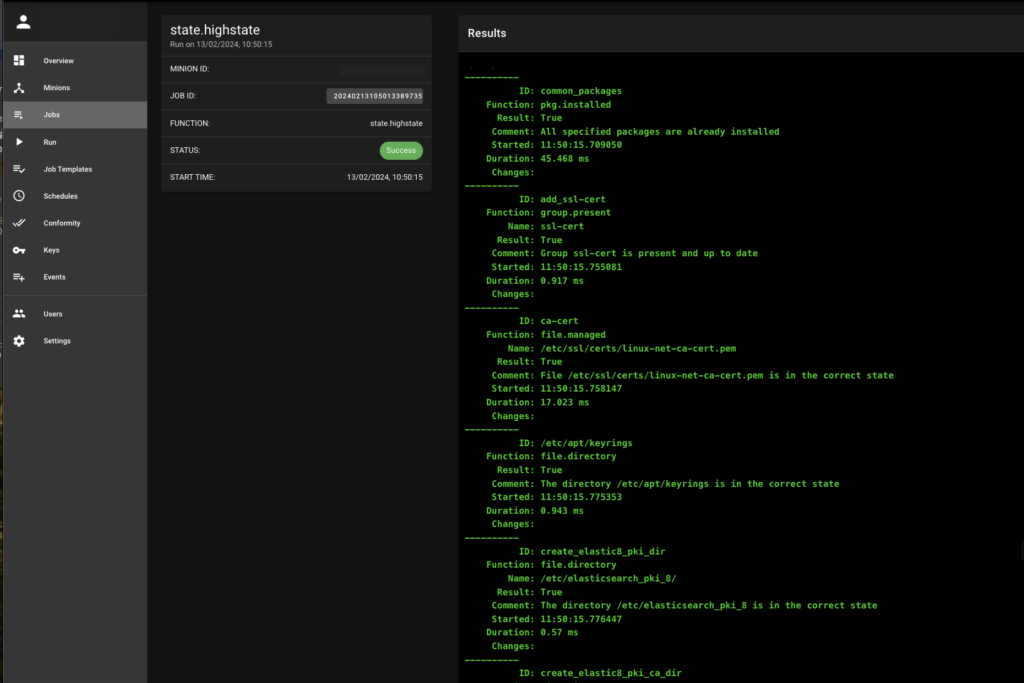
These actions can be automated through C4SAM‘s automation capabilities by running a simple one-liner or setting up a compliance state that is automatically executed during the compliance job.
Critical Vulnerability in Shim Boot Loader Affects Most Linux Distributions
Shim maintainers have released version 15.8 to address six security flaws, notably a critical bug identified as CVE-2023-40547 (CVSS score: 9.8). This vulnerability, discovered by Bill Demirkapi of the Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC), could facilitate remote code execution under specific conditions and bypass Secure Boot.
Numerous major Linux distributions including Debian, Red Hat, SUSE, and Ubuntu have issued advisories regarding this security flaw. Alan Coopersmith of Oracle highlighted the vulnerability’s root cause in shim’s http boot support, where attacker-controlled values in an HTTP response could trigger an out-of-bounds write primitive.
Demirkapi emphasized the ubiquity of the vulnerability, stating it affects every Linux boot loader signed in the past decade. Shim, a fundamental component acting as a first-stage boot loader on UEFI systems, is at the core of this issue.
CVE-2023-40547, according to firmware security firm Eclypsium, originates from mishandling of HTTP protocol, resulting in an out-of-bounds write that can potentially compromise the entire system. In a theoretical attack scenario, an adversary could exploit the flaw to load a vulnerable shim boot loader on the victim’s system or manipulate data on the EFI partition if granted adequate privileges.
Exploiting this vulnerability provides attackers with early-stage access during the boot process, allowing for the deployment of stealthy bootkits that grant extensive control over compromised hosts. Apart from CVE-2023-40547, shim version 15.8 also addresses five other vulnerabilities, each with its own implications and severity scores:
- CVE-2023-40546 (CVSS score: 5.3): Out-of-bounds read resulting in denial-of-service (DoS)
- CVE-2023-40548 (CVSS score: 7.4): Buffer overflow leading to potential crashes or data integrity issues on 32-bit processors
- CVE-2023-40549 (CVSS score: 5.5): Out-of-bounds read in authenticode function potentially triggering DoS
- CVE-2023-40550 (CVSS score: 5.5): Out-of-bounds read in Secure Boot Advanced Targeting (SBAT) validation leading to information disclosure
- CVE-2023-40551 (CVSS score: 7.1): Out-of-bounds read when parsing MZ binaries, possibly exposing sensitive data
Eclypsium highlighted the severity of these vulnerabilities, emphasizing that attackers gaining control before the kernel loads can bypass kernel and operating system controls, effectively granting privileged access.
Sources:
https://thehackernews.com/2024/02/critical-bootloader-vulnerability-in.html
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/critical-flaw-in-shim-bootloader-impacts-major-linux-distros/
Other blog posts
Critical Boot Loader Vulnerability in Shim
Critical vulnerability in the Shim boot loader What to do?...
Read MoreCybersecurity Trends 2024
Cybersecurity trends 2024 Intelligent & Resilient – Security through Automation...
Read MoreCybersecurity Kill Chain
What is a Cybersecurity Kill Chain? understanding, detecting, and preventing...
Read MoreWhy should SMEs be interested in cybersecurity awareness
Why should anyone target us? Why should SMEs be interested...
Read MoreTop 8 Prediction for Cybersecurity within the next 2 years
Top 8 Prediction for Cybersecurity within the next 2 years...
Read More